The Canine Communication: Understanding Dog Barking

As a vital aspect of canine communication, barking serves various purposes related to emotions and situations. Understanding the nuances of your dog’s bark can significantly enhance your relationship with them.
Decoding Your Dog’s Bark
Every bark carries a message. By paying attention to the pitch and tone, dog owners can often decipher their pet’s intent. Generally, a high-pitched bark indicates friendly interactions, suggesting excitement or playfulness. Conversely, a low-pitched bark or growl implies warning signs, such as danger or territorial instincts. Note that smaller dogs might have limitations in their vocal range when it comes to barking.
Understanding Excessive Barking
If your dog struggles with excessive barking, recognizing the underlying reasons is essential for appropriate intervention. While some breeds are naturally more vocal, others are quieter. Here are several common reasons dogs bark:
- Pain Bark: Dogs may vocalize when experiencing distress or discomfort. Increased barking or whining can signify underlying health issues.
- Alarm Bark: A natural reaction to perceived threats, this bark typically escalates in pitch as the danger approaches. Alarm barking can be closely related to territorial behaviors.
- Boredom Bark: Dogs confined to limited spaces or lacking stimulation often bark out of boredom. This behavior can lead to destructive actions if left unaddressed.
- Fearful Bark: Triggered by sudden noises or unfamiliar sights, fearful barking can reflect anxiety. Signs of fear may accompany these vocalizations, such as a rigid body and retracted ears.
- Fun Bark: A happy, excited bark often occurs during play or when greeting new friends. This type of barking is usually high-pitched and accompanied by wagging tails and friendly demeanor.
Identifying Barking Patterns
Different types of barking can hint at various emotional states:
Pain Bark: When a dog is in pain, vocalizations may increase, including whining or barking. Sudden changes in your dog’s vocal habits warrant a veterinary evaluation.
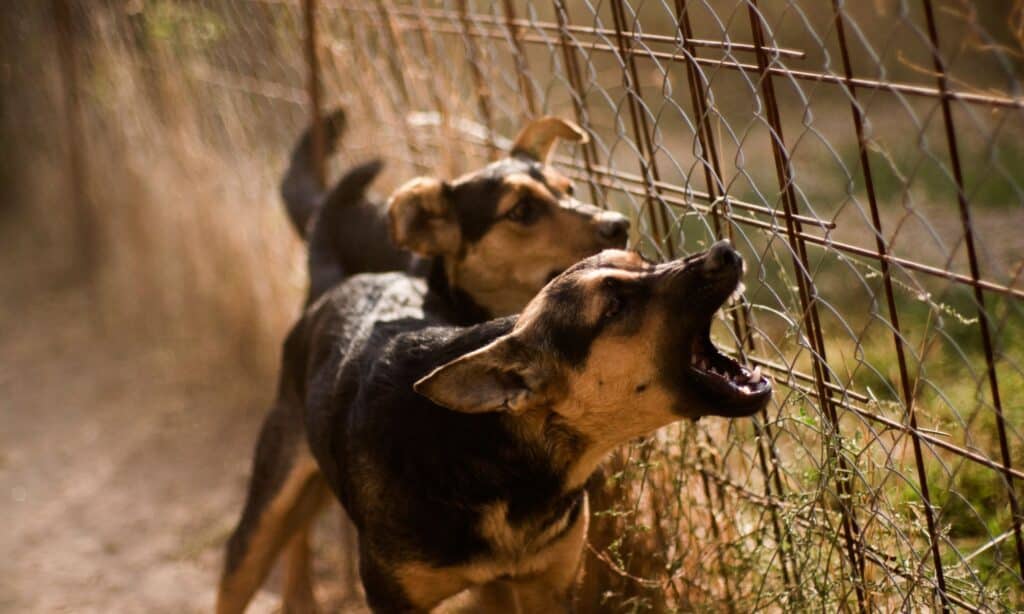

Alarm Bark: Indicative of outside disturbances, alarm barking signals an alert to any perceived threat approaching the home or owner.

Boredom Bark: Dogs not engaged in stimulating activities may resort to incessant barking out of frustration, leading to further behavioral issues.

Fearful Bark: Continuous barking in the presence of fear can escalate, often accompanied by anxious body language.

Fun Bark: Often featuring higher pitches and joyful tones, fun barking is common during playtime or joyful interactions.
Conclusion
Ultimately, understanding your dog’s barking patterns can enhance communication and bond between you and your furry friend. If excessive barking persists, consulting with a veterinarian is advisable to eliminate potential medical concerns before addressing behavioral modifications.












